Exploring how the computational power of modern NVIDIA® Quadro RTX™ GPUs is driving a new approach to design and engineering, with simulation at the heart of the decision making process
Despite major advances in design and engineering technology, the use of analysis and simulation is often left to the latter stages of product development. This could be for verification of a final design or even for the forensic role of working out why a part failed or a product was recalled.
But it’s early on in a product development workflow that analysis and simulation can have the most impact, as this is when the development process is highly iterative and unstructured and new ideas and forks in development vectors happen very quickly. By using analysis and simulation to answer simple questions like ‘is a design concept worth pursuing?’, good ideas can quickly be sorted from the bad, giving talented multi-disciplinary teams the vector they need to proceed with confidence.
This is well-illustrated by an example of an engineering team working on a new model of a transportation product. The powertrain is the focus and the product management team decides there are two main options for the cylinder head – the same configuration or roughly the same components with different alignment angles. But how does that seemingly simple variable of alignment angle influence important factors such as combustion, performance, efficiency and vibration?
Analysis and simulation have long been able to answer these questions, but it has traditionally taken weeks of pre-processing, loading case definition and iterative solves to get there. What if an existing design could be chopped into shape and simulated to give the team’s decision some grounding in real world results, in a time frame that could truly influence the decision-making process?
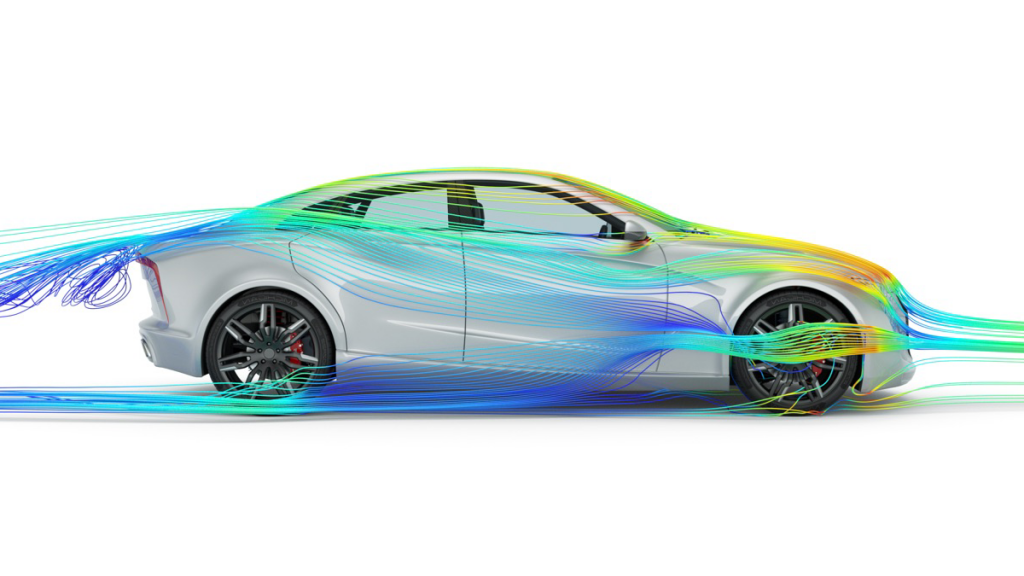
Ansys Discovery Live laid the foundations for change with a completely new approach to simulation that delivers ‘instantaneous’ results by harnessing the parallel processing capabilities of a workstation’s Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). With NVIDIA® Quadro RTX™ GPUs, based on the NVIDIA Turing™ GPU architecture, designers and engineers can get real time feedback on the performance of their designs through static structural, static and transient thermal and fluid flow analyses.
The technology can be seamlessly integrated with design. In PTC Creo Simulation Live, for example, the power of Ansys’s real time simulation technology is embedded within the CAD modelling environment, so the impact of every design change can be seen instantly. It means designers and engineers can quickly experiment with many alternatives and narrow down design options. Most importantly, because this is being done early on in the design process it can result in dramatic time and cost savings. NVIDIA GPUs are enabling interactive product design in other areas, including Ansys SPEOS Live Preview that predicts the illumination and optical performance of systems in real-time.
NVIDIA GPUs are also being used to solve even more complex simulations; and there are many computer-aided engineering (CAE) software tools that can take advantage of its enormous computational capabilities. Altair recently enhanced the GPU support for Altair AcuSolve, its high-end, general-purpose Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software that helps engineers simulate fluid flow with turbulence and heat transfer. These new enhancements specifically leverage NVIDIA Quadro RTX GPUs to solve computational problems up to four-times faster than CPU-only configurations.
The impact on product development can be huge. Large-scale CFD simulations which previously took days can now be completed overnight. Multiple design options can be explored in parallel and aesthetic decisions backed up by informed engineering decisions at the formative stages where they can have the biggest impact.
NVIDIA Quadro RTX GPUs offer industry-leading performance to ensure engineers can set up, test, and iterate on simulations more quickly than ever before. While a single Quadro RTX GPU can help speed-up simulations, multiple Quadro RTX GPUs can lead to an even more dramatic reduction of solve times.
NVIDIA RTX Server is a new reference design that can host multiple NVIDIA Quadro RTX 6000 or 8000 GPUs to deliver unprecedented performance at a fraction of the cost, space and power requirements of traditional CPU-based solutions. But RTX Server is much more than just a powerful server for simulation. Its highly flexible design means it can support many different workflows and roles.
By day, the resources can be virtualised, giving individual members of an engineering team access to their own powerful NVIDIA Quadro virtual workstation which can be accessed from any device, anywhere. Then, by night, all of the resources in RTX Server can be pooled to solve complex engineering problems at lightning fast speeds with applications such as Altair ultraFluidX and Altair nanoFluidX. And it’s not just limited to simulation. RTX Server can even be used for visualisation for interactive real-time ray tracing or batch processing of frames using the full complement of cores in a Quadro RTX GPU – RT Cores for accelerating ray tracing operations, Tensor Cores for AI denoising as well as the standard CUDA cores. Applications include Autodesk VRED, Altair Thea-Render and Luxion KeyShot.
From design-led analysis to complex multiphysics studies and large-scale CFD, GPUs are helping usher in a new dawn for simulation. With a dramatic reduction in solve times, in some cases instant, designers and engineers are now able to make much better informed decisions at the frenetic early stages of product development. And with more ideas, more iterations and the convergence of aesthetic design, functional design and performance engineering, this will ultimately lead to better quality products in a shorter time-frame through a more cost-effective process.
To learn more, visit these resources: