MI:Additive Manufacturing can analyse data to determine mechanical properties for CAE and design optimisation for production
Granta Design has announced MI:Additive Manufacturing, a software solution aimed at improving repeatability in the additive manufacturing industry by overcoming data challenges, such as logging materials and process information.
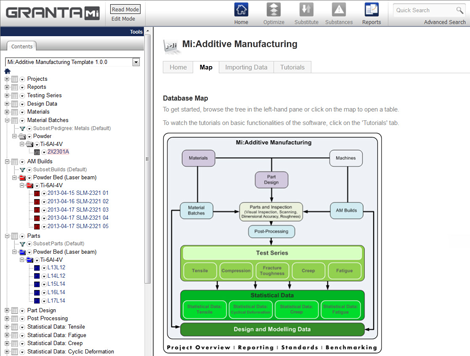
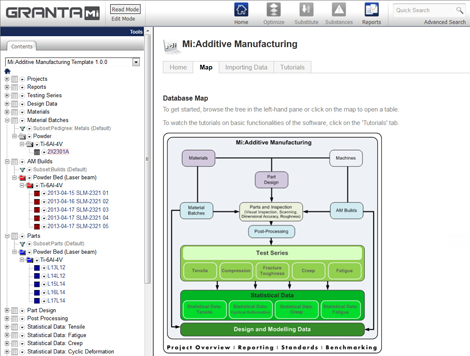
The MI:Additive Manufacturing workflow begins by importing ‘logfiles’ directly from 3D printers. The system automatically stores process parameters, extracts logged data for specific builds, links this information to supplier data on the batches of material used to make a part, and captures testing and inspection results.
This data can feed into statistical analyses that determine mechanical properties, which can be exported to simulation codes and the results can be captured for use in optimising part design and production.

Granta has been participating in a multinational collaborations to help better additive manufacturing of metal parts
Improved efficiency and repeatability are the goals, with the technology combining with the existing Granta MI materials information management tools.
Granta has been participating in a multinational collaborations between corporations and research institutions to help develop the new additive manufacturing technology.
One such programme, AMAZE, has seen 28 European companies and institutions developing rapid production of large defect-free additively-manufactured metallic components
Granta’s technology was used to capture and share the knowledge on materials, processes, and properties to enable data comparison, improvement of production knowledge, refinement of processes, integration of simulation activities, and improved coordination of the R&D program.
“MI:Additive Manufacturing combines our core strength in materials information management with practical knowledge of Additive Manufacturing data gained from our collaborative projects, and work with some of our leading customers”, comments Dr Patrick Coulter, chief operating officer at Granta Design.
“The great news is that this will allow us to help many other customers who have expressed an interest in Additive Manufacturing, and have been asking us for a solution to manage their data in this area.”